Urology is a field of medicine dealing with the urinary system in both men and women, as well as the reproductive system of men. Urological diseases require both a medical and surgical approach to treatment. Patients with urological diseases may be newborns, children, adolescents, adults, or elderly.
Management of urological diseases includes lifestyle measures, medication, and different types of surgical procedures such as endoscopy, laparoscopy, microsurgery, surgical excision, as well as reconstructive surgery. The variety of clinical problems, and the various approaches to patient care makes urology a fascinating specialty.

© Photo by Poongkodi Nagappan in 2008
There is overlap between urology and other specialties in areas such as pediatric urology, urogynaecology, retroperitoneal and pelvic tumours. This can create confusion as to which specialist a patient should see. When patients seek expertise and experience, a reasonable surgeon would be able to
- Explain indications, risks and alternatives to proposed treatment
- Perform the recommended surgical procedure in a competent and safe manner
- Anticipate and manage problems that may arise as a result of proposed treatment
The common urological conditions are urinary tract stones, urinary tract cancers, and benign prostate enlargement. These conditions, along with urological emergencies are often referred to as bread-and-butter urology, and a qualified urologist in Malaysia is expected to be competent in the management of such conditions. There are other areas of special interest that require additional learning, for example
- Andrology
- Neuro-urology
- Paediatric urology
- Reconstructive urology
- Renal transplantation surgery
- Female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery
UROLOGY CAREER PATHWAYS IN MALAYSIA
I qualified as a urologist in 2013. The only career pathway available to me at that time was after completion of general surgery training (on left) compared to the career pathway available now (on right).
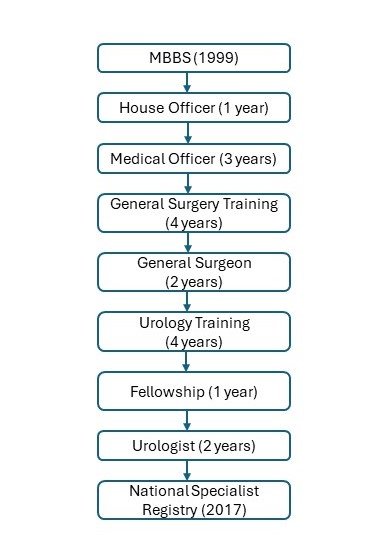
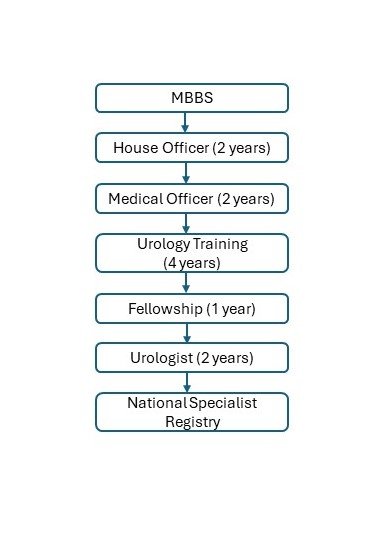
Whatever the career pathway, the important aspects to becoming a competent urologist are knowledge, surgical skills, and decision making, delivered with integrity (meaning a urologist is able to work within ethical and legal boundaries), and style (meaning having good communication skills and a professional manner).
